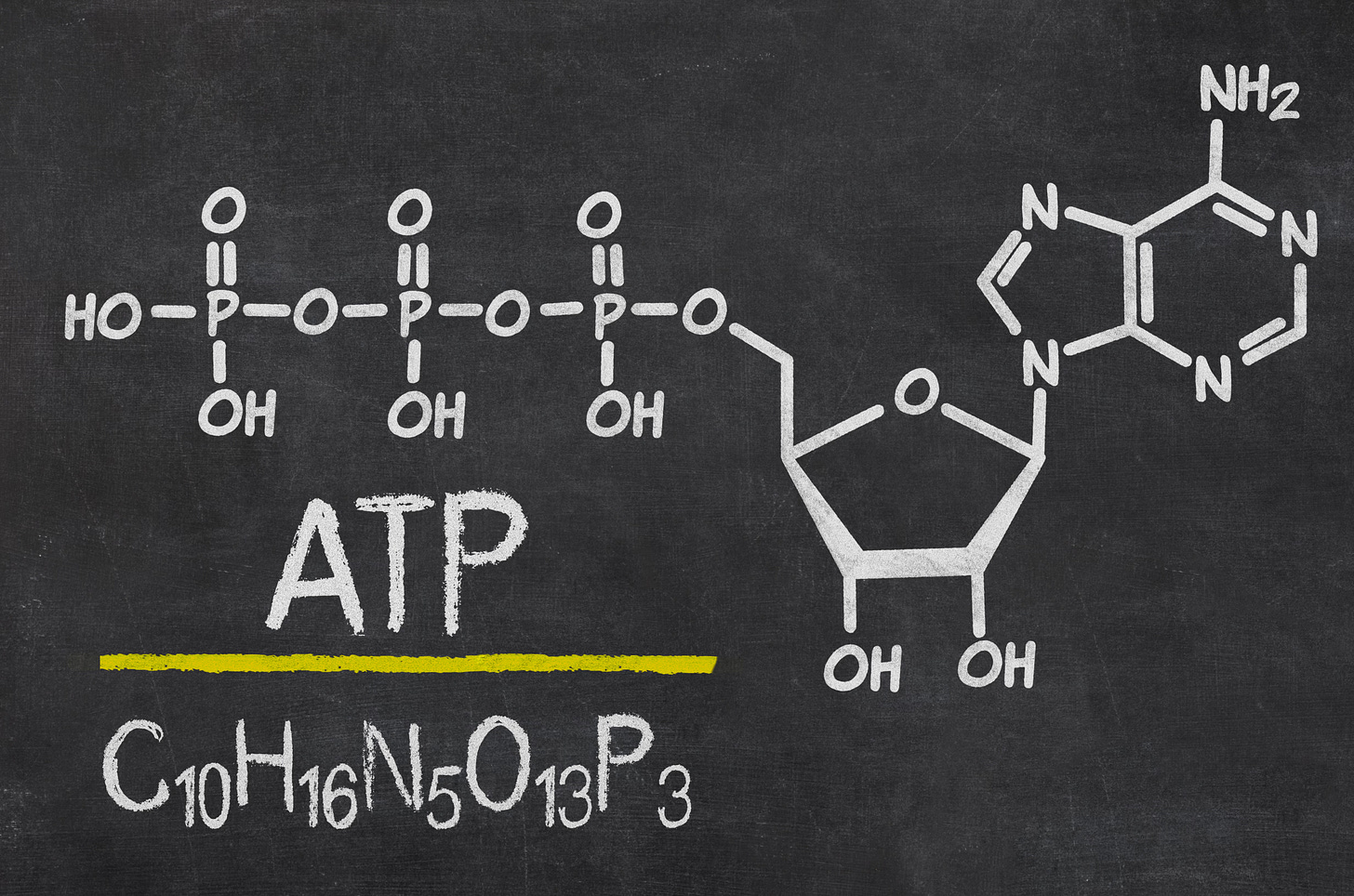
The Transformative Power of Meditation: Boosting ATP Production for Enhanced Energy Levels
Free Professionally Filmed and Edited Course on Meditation and Neuroplasticity
Introduction
In our fast-paced and stress-laden modern lives, the quest for sustained energy levels is a constant challenge. Many seek solutions in the form of energy drinks, caffeine, or quick fixes, often overlooking the profound impact that meditation can have on our energy …